Introduction
Welcome to the Arise Network documentation! We will introduce our network architecture, give examples of how to use our GraphQL interface, and provide step-by-step instructions to make your first transaction on our test network.
About Arise
Arise is a distributed network for hotels and the ecosystem of products and services around them. Our technology replaces the traditional API and cache based infrastructure in travel distribution with a model that is more similar to a distributed database that is shared by multiple organizations.
To accomplish this, we use a distributed ledger as our underlying data distribution model.
Our Network
Architecture
Our network is composed of connected nodes all running the same software. It has no central servers or single points of failure.
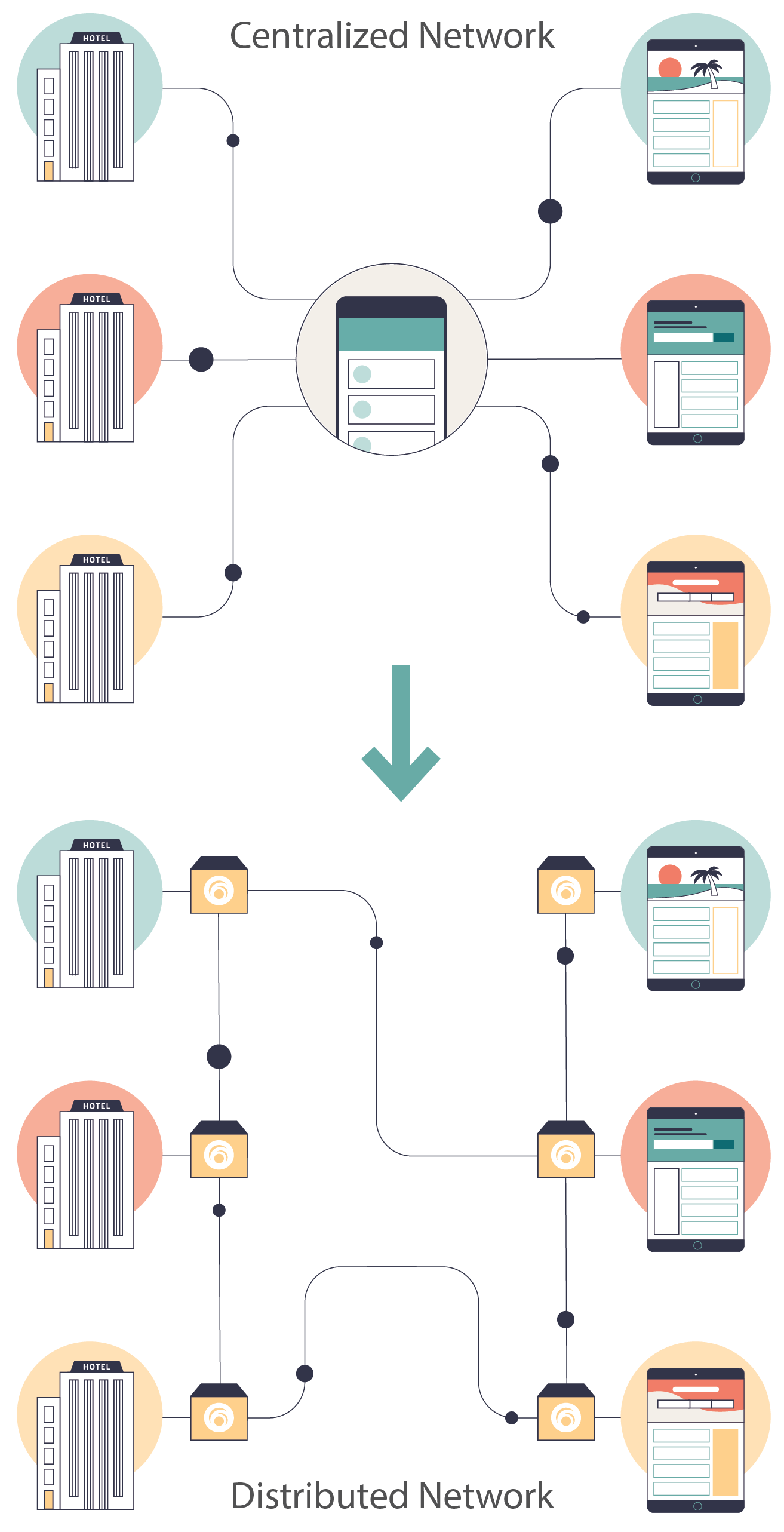
We use distributed ledger technology to build a shared, transparent database that multiple parties can read from and write to at the same time.
Our network is private and permissioned, meaning every connected node is linked to a known identity in the real world. New nodes need to be granted permissions by the network for read and write access.
We’ve built a distributed application on top of this shared database, that can use the stored ARI, Guest and Booking information to perform complex queries or to enforce detailed booking rules.
Our network supports 500+ TPS (writes) and does not suffer the same scaling issues as a centralized service would under heavy query load. The network is currently validating and confirming bookings transactions within 3 seconds of their submission.
Sensitive data is automatically stored in full compliance with GDPR and all traffic sent between nodes is encrypted.
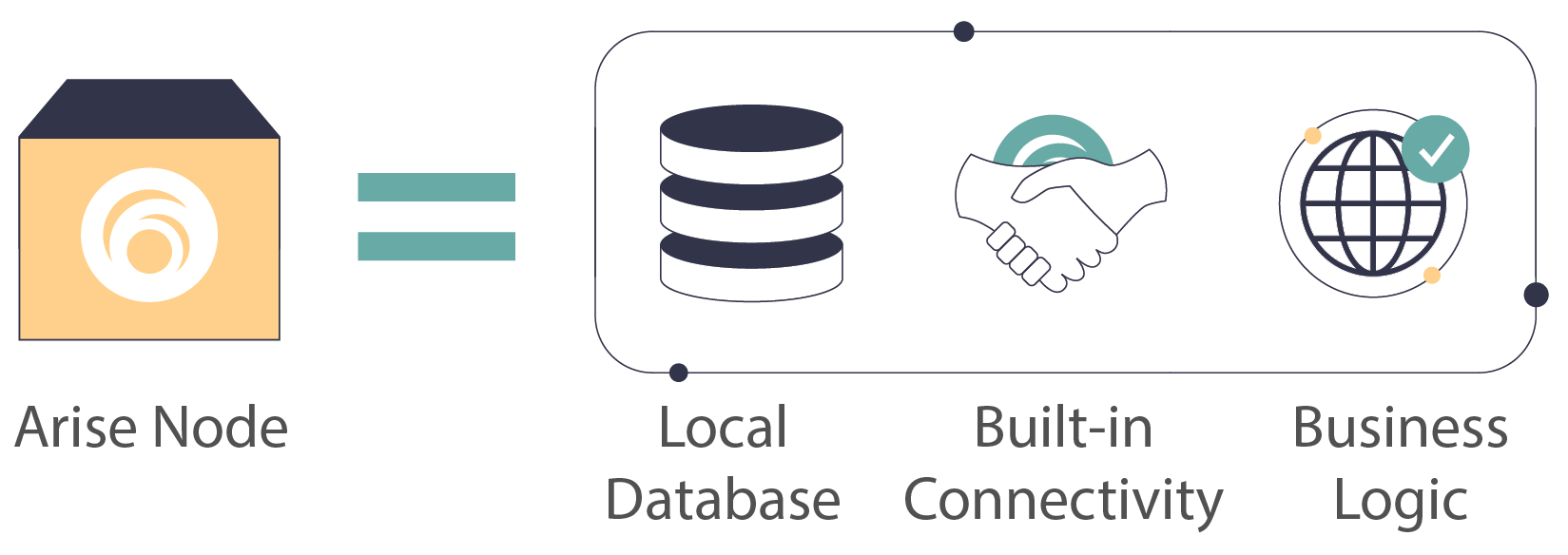
Each node provides a local cache of all hotel data and business logic that can perform complex, open-ended queries. Connectivity to other hotel applications on the network is built into the protocol.
Identity and Access
Access on the network is tied to the identity used to sign the transaction sent from each node. Each identity has a corresponding public / private key-pair that is signed by a Certificate Authority on the network. These identities are linked to specific Property or Partner records at the time of creation.
Any outside request for data or any transaction proposal without a valid signature will be rejected by the network.
Developer Experience
In order to make development on our network as simple as possible, we’ve abstracted away the underlying ledger and smart contracts behind a strongly typed GraphQL API.
The majority of 3rd party application integrations will only interact with our GraphQL API.
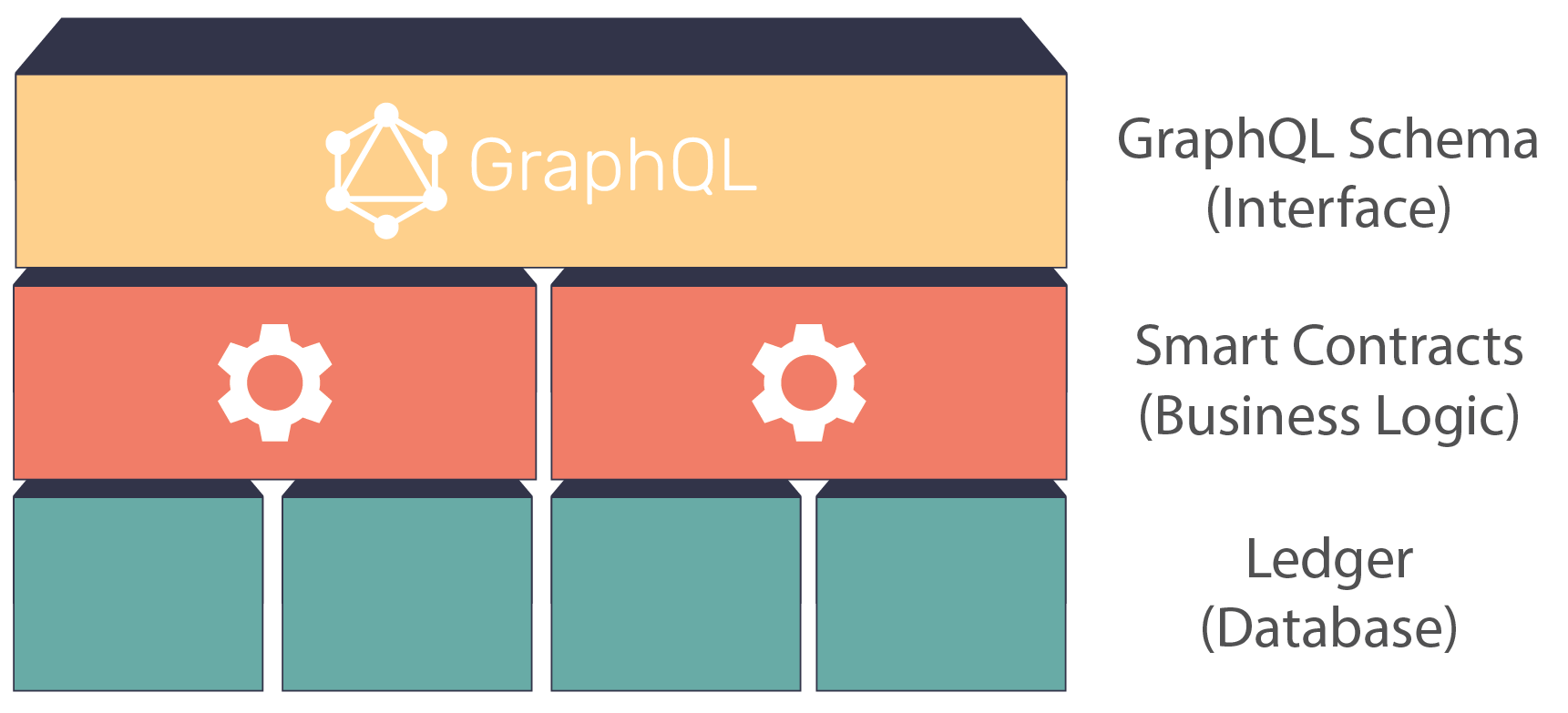
This GraphQL API makes it easy to explore the capabilities of the network while allowing developers to read and write information in a way that makes the most sense for their use case.
Our API
Why GraphQL
We’ve chosen to abstract away the network’s smart contracts behind an extensive GraphQL schema. GraphQL offers developers a way to interact with the network without needing to understand it’s underlying architecture or individual ‘smart contracts’ on the network. We also believe the rich set of developer tools in the GraphQL ecosystem will be a welcome change when compared to some of the tooling available for older API formats.
GraphQL is a query language for APIs and a runtime for fulfilling those queries with your existing data. GraphQL provides a complete and understandable description of the data in your API, gives clients the power to ask for exactly what they need and nothing more, makes it easier to evolve APIs over time, and enables powerful developer tools. - graphql.org
Benefits
No API Versioning
In GraphQL the client specifies which fields they would like in their response. GraphQL makes it easy to extend parts of the graph with new functionality or data in a way that won’t impact existing client integrations. Backwards compatibility is essential in this industry where hundreds of API integration can be built for a single client. The overhead of maintaining integrations can be significant and our goal is to reduce this load on development teams.
Strongly Typed Schema
Being strongly typed makes GraphQL queries less error prone and easier to validate before the client sends a request. A strongly typed data schema makes it possible to have rich integrations into IDEs/editors. Introspection queries make it possible to retrieve detailed information about allowed field values which is great for dynamically generating select elements in UI components.
Optimal Interactions with Smart Contracts
GraphQL allows us to optimize queries that otherwise would require multiple RESTful API calls and multiple interactions with smart contracts. Interacting with smart contracts (especially write transactions) can be complex. We’re often able to make specific optimizations around common data fetching patterns that allow us to combine multiple transactions on the network into a single transaction.
Excellent Tooling
The GraphQL ecosystem is growing. There are not only integrations for the strongly typed nature of GraphQL for editors and IDEs, but also standalone applications for GraphQL itself.
Using GraphQL
At first GraphQL can appear intimidating. Working with data as a graph can be quite a bit different from the common XML and RESTful APIs in the travel industry. We believe the advantages of having a self-documenting, strongly typed API with a thriving ecosystem of developer tools outweigh the initial learning curve.
We will provide examples throughout this documentation that any developer can run against a GraphQL endpoint on our test network to get started.
GraphQL Resources
Accessing Our API
Every node on our network runs it’s own standalone GraphQL interface and exposes an endpoint for queries and mutations at /graphql.
GraphQL queries are sent over https with the POST method.
Authentication
Example Authorization Header:
Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_GENERATED_JWT>
By default our network GraphQL interfaces are configured to check for a JWT Authorization header. This header must be included with each request made to the node’s /graphql endpoint. This includes GraphQL introspection queries that retrieve the available schema.
Payment Information
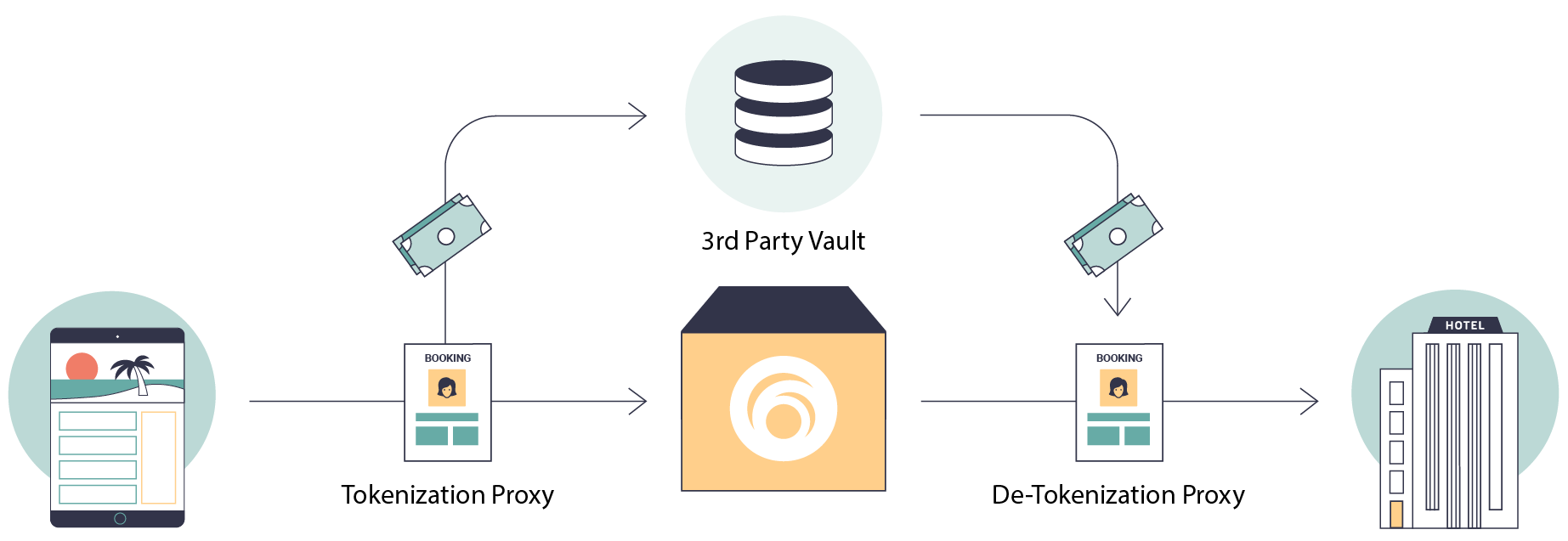
Sensitive payment information will often accompany Reservation mutations. Because of our architecture, storing this information within the network would make PCI compliance complicated. For this reason we use a PCI compliant tokenization service to transmit payment information between point of sale partners and hotels.
We use a PCI compliant third party that strips sensitive data from Reservation payloads and only reveals it to other PCI Compliant vendors. The network never touches the payment information.
Our Schema
Schema Conventions
Unique IDs
There are certain types on our network that are assigned globally unique IDs. This ID format follows UUID standards with an additional prefix.
Each unique ID on our network is composed of four uppercase letters that correspond to a specific network data-type followed by a standard UUID. This code can be used to fetch individual parts of the graph through the node interface without the need to fetch information through a root node. For example, if a developer wants to fetch a single Traveler from a Reservation, they could use the Traveler’s ID in the format TRAV-XXXXXXXX-XXXX-MXXX-NXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX and retrieve that information directly without re-fetching the parent reservation.
| Type Name | Code | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Partner | PART | A partner on the network. An identity linked to an OTA, RMS, PMS .etc |
| Property | PROP | A property on the network. Maps to one physical address. |
| Space Type | SPTP | A space type at a property. Equivalent to a room type |
| Space Type Rate | SPRT | A rate for a specific space type |
| Availability | AVAL | A unit of availability in a space type |
| Rate Plan | RATE | A rate plan |
| Rate Override | RAOR | A single day modification to a rate |
| Reservation | RSRV | A reservation |
| Traveler | TRAV | A Traveler. A Guest etc. |
| Product | PROD | A Product available for booking. |
| Internal | INTR | An internal ID used for special cases. |
Field Capitalization
Any field that has a capital letter as its first character like Traveler or SpaceType has a set of subfields. Any field that begins with a lowercase letter like name or value is a Scalar type (e.g. String, Integer, Enum )
Getting Started
All clients that interact with our network must be tied to a known identity. This includes clients interacting with our test network.
Request Access
Please reach out to us at contact@arise.travel and our team will follow up with you for the next steps. You’ll be asked to provide some of your business details and will be given test credentials afterwards.
We will also provide you with the steps to gain access to a node on our test network.
Test Network Limitations
The test network is shared between multiple organizations. Any data sent to the testnet should be considered public. Please do not submit transactions that contain sensitive PII or real booking details.
Testnet Rate Limits:
- A rate limit of 25,000 points per day is installed, 1 point corresponding to any subfield requested.
- Another rate limit of 1,000 points per request is fixed
- Mutation rate limit set to 1 per second and 30 per minute.
Using GraphQL
GraphQL Overview
query findAllProperties {
PropertiesConnection {
edges {
node {
id
name
websiteURL
}
}
}
}
The above query returns a JSON object structured like this:
{
"data": {
"PropertiesConnection": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"id": "PROP-fd17a3d9-9ebf-5338-a048-970fb301bd7c",
"name": "Steiningå",
"websiteURL": "http://www.steininga.com/"
}
}
]
}
}
}
In a nutshell, GraphQL lets you describe the shape of the data you want to fetch. Any API implementing the GraphQL spec defines a strongly typed schema that you can write queries and mutations against.
For example, the attached findAllPropeties query will fetch all the properties in the
network.
Note that query includes three fields that will be returned in the response:
idnamewebsiteURL
Interacting with the API
The Altair IDE
To help you quickly interact with the network and explore our schema, we’ve provided a built-in GraphQL IDE called Altair. It allows you to write GraphQL queries with auto-completion and provides in-line documentation of the API alongside your GraphQL documents. It’s the fastest way to prototype queries and mutations as you’re developing your application.
You can access the Altair IDE through the /altair endpoint in your browser.
Documentation is available in under Docs button on the right side of the IDE, or with Ctrl+click on any field in your current GraphQL document.
GraphQL Operations
The GraphQL spec defines three types of operations:
query: Fetches data from the API and returns it without modifying any of the underlying data.mutation: Performs an operation that can mutate the state of the underlying data.subscription: Watches for changes or events that occur on the underlying data.
A query will not have an impact on the network as a whole. It will only read data from a single node on the network and requires no additional confirmation steps before returning results. Query capacity scales as the network grows.
A mutation can (but not necessarily) mutate the state of the data on the network. These transactions will be validated by multiple nodes on the network and must be added to the ledger before they will return a result. For this reason it can take up to three seconds to receive a mutation confirmation. Multiple mutations can be run in parallel.
The subscription type reacts to events on the network, but doesn’t modify any data by itself.
Making a GraphQL Request
When you’re ready to integrate our API into your project, you will need to
POST your GraphQL requests to the /graphql endpoint. Any http client library can do this, but we recommend using a GraphQL client library in your language of choice.
There are a variety of tools that can make your day-to-day operations more efficient with GraphQL. You can either use simple GraphQL clients that will just bind the correct headers and parameters to the HTTP endpoint, or use more advanced libraries that generate code based on your GraphQL requests and retain type safety.
Connection Queries
GraphQL is all about exposing a graph of entities and their relationships. The Relay spec defines a set of rules to make it easier to work with one-to-many relationships, or any large collection of entities.
query propertiesForward {
PropertiesConnection(first: 10, after: "g2wAAAACaAJkA...") {
edges {
cursor
node {
id
name
}
}
pageInfo {
endCursor
hasNextPage
}
}
}
Both forward and backward pagination are supported by the Relay spec.
query propertiesBackwards {
PropertiesConnection(last: 10, before: "g2wAAAACaAJkA...") {
edges {
cursor
node {
id
name
}
}
pageInfo {
startCursor
hasPreviousPage
}
}
}
Relay enables cursor based pagination. It is different than traditional offset
based pagination that uses limit and offset parameters to generate the view
of a page. Instead, cursors are assigned to every returned entity and are used
to set the starting point of the page we want to fetch. In other words, instead
of providing the absolute position of the view in the dataset, we use a
relative positioning method for this view. This strategy enables
faster data retrieval for large datasets.
Because of this relative positioning, the dataset can be navigated in two different ways:
- Forward pagination, using the
firstandafterarguments : fetch the firstfirstn items after theaftercursor. - Backward pagination, using the
lastandbeforearguments : fetch the lastlastn items preceeding thebeforecursor.
Working With Mutations
For resources updates, we provide update and patch operations. They all have
very similar type signatures, but they behave in different ways:
updatebased mutations will replace the entity with the representation given in the payload. Be extremely cautious when using these mutations as they are potentially destructive.patchbased mutations will update the entity by merging the top-level fields of the payload with the existing entity in the network state. Top-level fields not included in the payload will remain unchanged, making partial updates possible.
Setting Up Test Data
Now that we’ve covered the basics of GraphQL, let’s add some data in the test network. You’ll only need access to the Altair IDE and GraphQL endpoint provided when you receive your testnet credentials.
This guide will help you get familiar with the Arise data schema and how every entity in the network is represented. This should also give you some rough idea on how partners will interact with each other within the network.
For the sake of this example, we’ll be interacting with the network as a Property Management System.
Create a Partner
mutation createPartner {
createPartner(payload: {
name: "My Cloud PMS"
CategoryTags: PMS
# ...
}) {
id
name
}
}
Example output of the above query:
{
"data": {
"createPartner": {
"id": "PART-1049c31f-b235-58e8-868b-4c5d8b9dba05",
"name": "My Cloud PMS"
}
}
}
In order for your service to be visible to the network, you’ll need to be register as a Partner. This will represent your company and will generate a unique ID.
Create a Property
mutation {
createProperty(payload: {
name: "Deluxe Resort & Spa"
PartnerExtRefs: {
partnerId: "PART-1049c31f-b235-58e8-868b-4c5d8b9dba05",
externalId: "255143"
}
Settings: {
checkReservationAvailability: true
}
# ...
}) {
id
PartnerExtRefs {
Partner {
id
}
externalId
}
}
}
Example output of the above query:
{
"data": {
"createProperty": {
"id": "PROP-fd17a3d9-9ebf-5538-a048-970fb301bd7c",
"PartnerExtRefs": {
"Partner" : {
"id": "PART-1049c31f-b235-58e8-868b-4c5d8b9dba05"
},
"externalId": "255143"
}
}
}
}
Now you need to register a hotel that your PMS manages. This is done by calling the createProperty mutation. You probably already have a unique identifier for the Property in your system and the schema allows you to store those mappings through the PartnerExtRefs field.
Query Your Property
# This query uses GraphQL variables to pass dynamic values into a static query
query getPropertyByExternalId($externalId: String!, $partnerId: partnerId!) {
PropertiesConnection(query: {
PartnerExtRefsList: {
partnerId: $partnerId
externalIds: [$externalId]
}
}) {
edges {
node {
id
name
# ...
}
}
}
}
When you want to fetch your property’s details on the network, you don’t have
to manage a mapping of the network’s identifiers to yours as the
PartnerExtRefs fields already contains them. You can then query the property
directly using the query argument of the PropertiesConnection query field.
Create Your SpaceType and RatePlan
Next, you’ll need to populate your hotel’s inventory on the network. This is
done by creating the SpaceType and RatePlan entities for each of your
Property instances.
Create a SpaceType
mutation createSpaceType ($propertyId: propertyId!) {
createSpaceType(
payload: {
propertyId: $propertyId
name: "Double Room"
isActive: true
Occupancy: { maxChildren: 1, minOccupants: 1, maxOccupants: 3 }
# ...
}
) {
id
name
}
}
First, create a SpaceType. This represents a room type, with all of the
details about the room: name, description, photos, occupancy and amenities.
Check the GraphQL docs for additional fields you can include in a SpaceType.
Create a RatePlan
mutation ($propertyId: propertyId!){
createRatePlan(payload: {
propertyId: $propertyId,
name: "-10% on taxes",
isActive: true,
Taxes: [{
name: "Test Percentage Tax",
percentage: 10,
sequenceNumber: 1
}]
}){
id
name
}
}
Next, you’ll need to create a RatePlan. This represents the type of rates
you’re going to distribute on the network.
RatePlan controls the high level details of a particular rate, like Taxes and policies. It does not include the actual prices.
Create a SpaceTypeRate
mutation createSpaceTypeRate (
$propertyId: propertyId!
$spaceTypeId: spaceTypeId
$ratePlanId: ratePlanId
) {
createSpaceTypeRate(
payload: {
propertyId: $propertyId
ratePlanId: $ratePlanId
spaceTypeId: $spaceTypeId
isActive: true
isAvailableToAllPartners: true
RatePeriods: [
{
startDate: "2022-01-01"
endDate: "2022-12-31"
timeUnit: DAILY
OpenToArrivalDOW: {
sunday: true
monday: true
tuesday: true
wednesday: true
thursday: true
friday: true
saturday: true
}
OpenForSaleDOW: {
sunday: true
monday: true
tuesday: true
wednesday: true
thursday: true
friday: true
saturday: true
}
OpenToDepartureDOW: {
sunday: true
monday: true
tuesday: true
wednesday: true
thursday: true
friday: true
saturday: true
}
RateAmounts: {
BaseGuestAmounts: [
{
minimumAdultTravelers: 1
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees: {
value: 11700 # = $117.00
currencyCode: USD
decimalPlaces: 2
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
) {
id
Property {
id
}
SpaceType {
id
}
RatePlan {
id
}
}
}
Now that you have created your SpaceType and RatePlan, you need to
create a link between them using a SpaceTypeRate. This is where the
actual pricing information is stored.
Set SpaceType Availability
mutation setAvailability($propertyId: propertyId!, $spaceTypeId: spaceTypeId!) {
setAvailability(
query: { propertyId: $propertyId }
payload: {
spaceTypeId: $spaceTypeId
startDate: "2022-01-01"
endDate: "2022-12-31"
count: 15
}
) {
date
count
}
}
Now set the availability of your SpaceType with the setAvailability mutation.
This example sets the same availability count for that entire time range, but you can
also pass an array in the payload to set different availability for different
days in a single call.
Search For Products
query getProducts($propertyId: [propertyId!]) {
PropertiesConnection(query: { PropertyIdList: $propertyId }) {
edges {
node {
ProductsConnection(
query: {
startDate: "2022-01-16"
endDate: "2022-01-18"
TravelerGroups: {
TravelerCount: { adults: 2 }
TravelerAges: [3]
}
}
) {
edges {
node {
id
startDate
endDate
SpaceType {
id
name
# ...
}
RatePlan {
id
name
# ...
}
TotalPrice {
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees {
value
currencyCode
decimalPlaces
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
At this point, you’ve completed your first configuration as a PMS. Now other partners can search for bookable Products at the property you’ve created.
Let’s put ourselves in the shoes of an Online Travel Agency. This agency can explore
available Products by searching for them under the Property.ProductsConnection
field and return there results back to their users.
Create a Reservation
mutation ($propertyId: propertyId!, $partnerId: partnerId!) {
createReservation(
payload: {
propertyId: $propertyId
# Partner ID of the OTA creating this reservation
# Note : on the main network, this is determined
# through the network identity
partnerId: $partnerId
startDate: "2022-01-16"
endDate: "2022-01-18"
SpaceStays: [
{
# Get this productId from a ProductConnection Query
productId: "PROD-79e237ad-5401-5404-819e-e39985aa5396"
startDate: "2022-01-16"
endDate: "2022-01-18"
StayRate: {
TotalPrice: {
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees: {
value: 23400 # = $234.00
currencyCode: USD
decimalPlaces: 2
}
}
}
TravelerCount: { adults: 2 }
TravelerAges: [3]
Traveler: {
Email: { address: "john@doe.com" }
PersonName: { surname: "John", Given: "Doe" }
}
}
]
}
) {
id
startDate
endDate
}
}
Now that a user has selected a Product to book, You can use the createReservation
mutation to create a Reservation, applying the terms defined in your RatePlan,
SpaceType and SpaceTypeRate items.
Notice that you need to provide the StayRate with the reservation. This ensures that there is
no disparity between the displayed and the actual price in the event the underlying price has changed during the booking process.
Traveler details are not stored immutably on the network, but instead are stored outside of the ledger in a separate collection that is GDPR compliant.
Retrieve Your Reservation
subscription watchReservations {
watchReservations(
propertyId: "PROP-fd17a3d9-9ebf-5538-a048-970fb301bd7c"
partnerId: "PART-1049c31f-b235-58e8-868b-4c5d8b9dba05"
) {
id
TravelerSummary {
PersonName {
Prefix
Given
Middle
surname
}
# ...
}
SpaceStays {
startDate
endDate
# ...
}
}
}
Back on the PMS side, you might want to be notified when a Reservation is made
on the properties you manage. This can be done through the watchReservations
GraphQL subscription. Subscribing to this GraphQL subscription will open a
WebSocket connection and the Arise Node will push messages to the listening
client whenever a new Reservation is made for that specific property.
Primary Types
Our network schema relies on a set of primary types that join together to build a complete set of information required to manage, display and book accommodation inventory.
This section will explain each type, its purpose and how it relates to the other primary types in our schema.
Partner
A Partner represents a non-accommodation entity that can access network data. This could be an organization, business or service. Partners can be enrolled as Members at specific Property entities on the network, granting them permissions to view and / or manipulate Property data.
An example would be an RMS (Revenue Management System) that has been given permission by a hotel to dynamically adjust its rates on the network as market conditions change. The RMS company can create a Partner record on the network and hotels can grant that Partner record access to their Property. The RMS will then be able to make adjustments to Property rates directly.
Property
A Property represents an accommodation has a set of bookable units available for booking. Hotels are the most common example, but a Property could represent less traditional lodging units like a house being listed as vacation rental.
A Property can grant access to Partner entities on the network.
SpaceType
A SpaceType defines a group of similar bookable units at a Property. An example would be a group of “King Rooms” at a Hotel. Availability of a SpaceType can be set on a day-by-day basis, and RatePlans can be linked with SpaceTypes using a SpaceTypeRates entity.
SpaceType entities contain text and MultimediaContent to display to potential Travelers during the booking process.
RatePlan
A RatePlan is assigned to a Property and contains information about its BookingPolicies (Cancellation, No-Show etc.) and BookingRules (DOW rate availability, and arrival offsets). RatePlan entities hold information about Tax and Fee structures, but do not directly contain pricing information for SpaceTypes. See SpaceTypeRates for pricing information.
SpaceTypeRates
SpaceTypeRate entities set the price for SpaceType units. They assign a price with conditions to a combination of RatePlan and SpaceType entities.
See RatePeriods for more information on the conditions and restrictions available.
Availability
Availability entities contain the number of available bookable units for a SpaceType for a single date.
Product
Product entities are generated when the network is queried for available accommodation and pricing information. Products are generated from a set of conditions based on the query being run along with SpaceType, Availability, RatePlan and SpaceTypeRates configurations. Products are ultimately the entities being sold to Travelers to create Reservations.
Traveler
A Traveler entity represents a person in the real world. Travelers are equivalent to Guests in other systems. They contain information that can link a record on the network to a real-world individual. Traveler information is sensitive and is only stored by reference on our network in order to comply with privacy and data regulations like GDPR. This is the only record type that can be completely deleted from the network.
Reservation
A Reservation entity holds information about a group of SpaceStays at a Property. It contains information related to the BookingRestrictions, BookingPolicies and Commission agreed upon when the Reservation was created.
SpaceStay
A SpaceStay entity links a purchased Product to a set of Traveler records. SpaceStays contain information about the stay dates, SpaceType and RatePlan booked, along with Traveler requests pertaining to a particular stay at a Property.
Common Types
These types are reused throughout the schema to hold information related to different entities in a common format.
MultimediaCollection
MultimediaCollection entities contain information about images or video content that can be displayed to the end user.
They contain titles, descriptions and tags related to the content and also a set of MultimediaVersion entities that contain external URLs pointing to the linked content in different sizes / variations.
All contents is stored by reference outside of the network.
Financial Types
CurrencyAmount
{
"value": 12900,
"currencyCode": "USD",
"decimalPlaces": 2
}
This is equivalent to a currency amount of 129.00 USD
{
"value": 2977152,
"currencyCode": "VND",
"decimalPlaces": 0
}
This is equivalent to a currency amount of 2977152 VND
| Field Name | Type | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| value | Integer | The original currency amount multiplied by 10^decimal |
| currencyCode | String | ISO 4217 Currency Code |
| decimal | Integer | ISO 4217 Currency decimal places |
CurrencyAmount entities are reused throughout the schema to represent a monetary amount.
RatePeriod
RatePeriod entities contain low level detail about rates and the set of conditions that restrict those rates for booking as a Product.
RatePeriods are found in the SpaceTypeRate entity and are configured as set of conditions and RateAmounts specified for a date range.
Available conditions are:
| Condition Name | Type | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| OpenToArrivalDOW | DOW toggle | Determines if RatePeriod is available based on startDate of a Reservation |
| OpenForSaleDOW | DOW toggle | Determines if RatePeriod is available based on through range of a Reservation |
| OpenToDepartureDOW | DOW toggle | Determines if RatePeriod is available based on endDate of a Reservation |
| minLOS | Integer | The minimum number of nights in a Reservation |
| maxLOS | Integer | The maximum number of nights in a Reservation |
RateAmount
RateAmount entities contain information about pricing restrictions based on number and age of Travelers.
There are two sub-entities BaseGuestAmounts and AdditionalGuestAmounts.
BaseGuestAmounts specifies pricing information for a specific number of Travelers based on their defined ageGroup.
AdditionalGuestAmounts specifies pricing information for a each additional Traveler beyond what is defined in BaseGuestAmounts based on that Travelers defined ageGroup.
RateOverride
A RateOverride is an entity used to adjust pricing specified for a single date. It can be used to change the rate available to a specific Partner or to open or close a rate for a single date.
Taxes and Fees
Tax and Fee entities contain information about tax and fee structures used in RatePlan, Product and Reservation entities.
Tax and Fee entities can be related to each other based on the sequenceNumber and AdditionallyAppliedTo fields. These fields are used to define “tax-on-tax” scenarios, where the amount of one calculated tax is based on the outcome of another tax total.
Review the GraphQL schema field descriptions for a complete set of options for Tax and Fee entities.
We will be adding examples in the near future to expand on the configuration needed for common tax structures.
Property Examples
Complete detail of our entire schema and each individual field along with its type can be found by exploring the Playground IDE included with each node.
Find Property
A simple example of querying for data about a specific Property with a known ID.
query {
PropertiesConnection( query: {
PropertyIdList: ["PROP-20c7c5f5-8b11-56aa-aba3-9f3554c8de14"]
}){
edges {
node {
id
name
Location {
Address {
AddressLine
street
city
StateProv {
name
value
}
country
}
Position {
latitude
longitude
}
}
}
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"PropertiesConnection": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"id": "PROP-20c7c5f5-8b11-56aa-aba3-9f3554c8de14",
"name": "Hotel Arise",
"Location": {
"Address": {
"AddressLine": [
"Hotel Arise",
"660 York Street",
"San Francisco, CA 94110",
"United States"
],
"street": "660 York Street",
"city": "San Francisco",
"StateProv": {
"name": "California",
"value": "US-CA"
},
"country": "US"
},
"Position": {
"latitude": -33.9314534,
"longitude": 151.1904941
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
In this example we will fetch detailed information about:
- Location
Property Content
Fetching additional information about a Property's Amenities and available Multimedia Content.
query {
PropertiesConnection( query: {
PropertyIdList: ["PROP-20c7c5f5-8b11-56aa-aba3-9f3554c8de14"]
}){
edges {
node {
id
name
Amenities
MultimediaCollection {
type
Versions {
url
}
title
Description {
value
language
}
}
}
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"PropertiesConnection": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"id": "PROP-20c7c5f5-8b11-56aa-aba3-9f3554c8de14",
"name": "Hotel Arise",
"Amenities": [
"AIR_CONDITIONING",
"POOL",
"DISCO",
"EXERCISE_GYM",
"COFFEE_SHOP"
],
"MultimediaCollection": {
{
"type": "IMAGE",
"Versions": [
{
"url": "https://arise.travel/assets/hero.svg"
}
],
"title": "Our Beautiful Hotel",
"Description": [
{
"value": "Our historic hotel is in a perfect location for everything you need.",
"language": "eng"
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
In this example we will fetch detailed information about:
- Amenities
- Multimedia Content
Filter Properties
query {
PropertiesConnection( query:{
Location:{
latitude: -33.9314500,
longitude: 151.1904900,
distance: 1,
distanceUnits: MILES
}
}){
edges {
node {
id
name
Location {
Position {
latitude
longitude
}
}
}
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"PropertiesConnection": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"id": "PROP-20c7c5f5-8b11-56aa-aba3-9f3554c8de14",
"name": "Hotel Arise",
"Location": {
"Position": {
"latitude": -33.9314534,
"longitude": 151.1904941
}
}
}
},
{
"node": {
"id": "PROP-dc7fdc57-7c0d-5e8c-b472-2245529768f8",
"name": "York Street Motel",
"Location": {
"Position": {
"latitude": -33.9314539,
"longitude": 151.1904934
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
An example of querying for a list of Properties within a geographic area.
This query will return multiple Property objects returned as a node inside an edge wrapper. This configuration follows the Relay Specification for GraphQL pagination.
Update a Property
mutation {
updateProperty( query: {
propertyId: "PROP-d4d6d2b6-3e5a-5683-8c90-eab678ba9c9a"
},
payload: {
PartnerExtRefs: [{
partnerId: "PART-1e0ddd4d-eeee-58fa-b4de-dfb08057ccdd",
externalId: "255143"
}]
name: "Renamed hotel"
}){
id
name
PartnerExtRefs {
Partner {
name
}
externalId
}
}
}
mutation {
patchProperty( query: {
propertyId: "PROP-d4d6d2b6-3e5a-5683-8c90-eab678ba9c9a"
},
payload: {
PartnerExtRefs: [{
partnerId: "PART-1e0ddd4d-eeee-58fa-b4de-dfb08057ccdd",
externalId: "255143"
}]
name: "Renamed hotel"
}){
id
name
PartnerExtRefs {
Partner {
name
}
externalId
}
}
}
These two mutations may seem really similar, but the first one updateProperty is replacing the Property data by the given payload, and will clear every top-level field not provided. As an example, if the property had Location or websiteURL they will be null after.
The second one patchProperty will perform a merge on top level fields, in this case, updating only the name of the property.
Use patchProperty for partial updates, if for some reason you need to change the whole object, use updateProperty.
Create a SpaceType
mutation {
createSpaceType(payload: {
propertyId: "PROP-d4d6d2b6-3e5a-5683-8c90-eab678ba9c9a",
name: "Test Space Type",
PartnerExtRefs: [{
partnerId: "PART-1e0ddd4d-eeee-58fa-b4de-dfb08057ccdd",
externalId: "BDC-444-444"
}]
}) {
id
name
PartnerExtRefs{
Partner {
name
}
externalId
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"createSpaceType": {
"id": "SPTP-274656d9-7053-5af5-a9e8-fc0fa2e864a6",
"name": "Test Space Type",
"PartnerExtRefs": [
{
"Partner": {
"name": "My Cloud PMS"
},
"externalId": "BDC-444-444"
}
]
}
}
}
In this example we will add a new SpaceType to an existing Property that has been created on the network. A SpaceType is equivalent to a Room Type in some other systems. It contains information about a certain type of space available for booking at a Property. SpaceTypes have a certain number of bookable units available for each date. The number of units available for booking can be set using Availability.
ARI Examples
Availability, rates and / or inventory (ARI) determines the Products available for booking by a Traveler at a Property.
Availability sets the number of bookable units available for a specific SpaceType at a Property. RatePlans and RatePeriods are used to define the amount a Traveler must pay to create a Reservation.
Complete detail of our entire schema and each individual field along with its type can be found by exploring the Playground IDE included with each node.
Update Availability
mutation {
setAvailability(query: {
propertyId: "PROP-20c7c5f5-8b11-56aa-aba3-9f3554c8de14"
},
payload: {
spaceTypeId: "SPTP-47185db3-63cc-5d91-9cee-eecf04b7e7e5",
startDate: "2022-10-01",
endDate: "2022-10-10",
count: 10
})
{
date
count
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"setAvailability": [
{
"date": "2022-10-01",
"count": 10
},
{
"date": "2022-10-02",
"count": 10
},
{
"date": "2022-10-03",
"count": 10
},
{
"date": "2022-10-04",
"count": 10
},
{
"date": "2022-10-05",
"count": 10
},
{
"date": "2022-10-06",
"count": 10
},
{
"date": "2022-10-07",
"count": 10
},
{
"date": "2022-10-08",
"count": 10
},
{
"date": "2022-10-09",
"count": 10
},
{
"date": "2022-10-10",
"count": 10
}
]
}
}
This example sets the Availability count for a specific SpaceType at a Property for a given date range.
The response expands that range into day-by-day breakdown of the resulting Availability
Create a RatePlan
mutation {
createRatePlan(payload: {
propertyId: "PROP-20c7c5f5-8b11-56aa-aba3-9f3554c8de14",
name: "Best Available Rate",
isActive: true,
MealsIncluded: {
breakfastIncluded: true
},
BookingRules: {
ArrivalOffset: {
minimumDaysInAdvance: 30
}
},
BookingPolicies: {
CancellationPolicy: {
Deadline: {
timePeriodStart: 7,
timePeriodUnits: DAYS,
deadlineType: BEFORE_ARRIVAL
},
numberOfNights: 1,
basisType: NIGHTS
}
}
})
{
id
name
isActive
MealsIncluded {
breakfastIncluded
}
BookingRules {
ArrivalOffset {
minimumDaysInAdvance
}
}
BookingPolicies {
CancellationPolicy {
Deadline {
timePeriodStart
deadlineType
}
numberOfNights
basisType
}
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"createRatePlan": {
"id": "RATE-8f453169-b3e2-5a27-b392-146e6909b756",
"name": "Best Available Rate",
"isActive": true,
"MealsIncluded": {
"breakfastIncluded": true
},
"BookingRules": {
"ArrivalOffset": {
"minimumDaysInAdvance": 30
}
},
"BookingPolicies": {
"CancellationPolicy": {
"Deadline": {
"timePeriodStart": 7,
"deadlineType": "BEFORE_ARRIVAL"
},
"numberOfNights": 1,
"basisType": "NIGHTS"
}
}
}
}
}
This example creates a new RatePlan that includes breakfast, must be booked 30 days in advance and has a CancellationPolicy stating that any Reservation made with this RatePlan will be charged a penalty of one nights rent if canceled within 7 days of arrival.
Add a RatePlan to a SpaceType
mutation {
createSpaceTypeRate(
payload: {
propertyId: "PROP-5169fad0-81c9-5bc6-92c7-e3a130973990"
ratePlanId: "RATE-0a5d5d1f-25de-55b4-a8e9-76c047cc9e5b"
spaceTypeId: "SPTP-d43b797d-267a-5a33-a1b6-7dc054c6f55b"
isActive: true
RatePeriods: [
{
startDate: "2022-10-01"
endDate: "2022-10-10"
timeUnit: DAILY
minLOS: 1
RateAmounts: {
BaseGuestAmounts: [
{
minimumAdultTravelers: 2
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees: {
value: 12900
currencyCode: USD
decimalPlaces: 2
}
}
]
AdditionalGuestAmounts: {
AmountPerAdultTraveler: {
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees: {
value: 2000
currencyCode: USD
decimalPlaces: 2
}
}
AmountPerChildTraveler: {
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees: {
value: 1000
currencyCode: USD
decimalPlaces: 2
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
) {
isActive
RatePeriods {
minLOS
startDate
endDate
timeUnit
RateAmounts {
BaseGuestAmounts {
minimumAdultTravelers
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees {
value
currencyCode
decimalPlaces
}
}
AdditionalGuestAmounts {
AmountPerAdultTraveler {
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees {
value
currencyCode
decimalPlaces
}
}
AmountPerChildTraveler {
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees {
value
currencyCode
decimalPlaces
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"createSpaceTypeRate": {
"isActive": true,
"RatePeriods": [
{
"minLOS": 1,
"startDate": "2022-10-01",
"endDate": "2022-10-10",
"timeUnit": "DAILY",
"RateAmounts": {
"BaseGuestAmounts": [
{
"minimumAdultTravelers": 2,
"AmountAfterTaxesAndFees": {
"value": 12900,
"currencyCode": "USD",
"decimalPlaces": 2
}
}
],
"AdditionalGuestAmounts": {
"AmountPerAdultTraveler": {
"AmountAfterTaxesAndFees": {
"value": 2000,
"currencyCode": "USD",
"decimalPlaces": 2
}
},
"AmountPerChildTraveler": {
"AmountAfterTaxesAndFees": {
"value": 1000,
"currencyCode": "USD",
"decimalPlaces": 2
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
This example creates a SpaceTypeRate with a single RatePeriod that defines a rate amount on a DAILY basis. The BaseGuestAmount value sets the price for up to two ADULT occupants. The AdditionalGuestAmount values define the incremental price for an additional ADULT or CHILD occupant.
Length-of-Stay Based Rates
mutation {
createSpaceTypeRate(
payload: {
propertyId: "PROP-5169fad0-81c9-5bc6-92c7-e3a130973990"
ratePlanId: "RATE-0a5d5d1f-25de-55b4-a8e9-76c047cc9e5b"
spaceTypeId: "SPTP-d43b797d-267a-5a33-a1b6-7dc054c6f55b"
isActive: true
RatePeriods: [
{
startDate: "2022-10-11"
endDate: "2022-10-20"
timeUnit: DAILY
minLOS: 1
RateAmounts: {
BaseGuestAmounts: [
{
minimumAdultTravelers: 2
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees: {
value: 12900
currencyCode: USD
decimalPlaces: 2
}
}
]
}
}
{
startDate: "2022-10-11"
endDate: "2022-10-20"
timeUnit: FULL_DURATION
minLOS: 2
maxLOS: 2
RateAmounts: {
BaseGuestAmounts: [
{
minimumAdultTravelers: 2
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees: {
value: 21900
currencyCode: USD
decimalPlaces: 2
}
}
]
}
}
{
startDate: "2022-10-11"
endDate: "2022-10-20"
timeUnit: FULL_DURATION
minLOS: 3
maxLOS: 3
RateAmounts: {
BaseGuestAmounts: [
{
minimumAdultTravelers: 2
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees: {
value: 30900
currencyCode: USD
decimalPlaces: 2
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
) {
isActive
RatePeriods {
minLOS
maxLOS
startDate
endDate
timeUnit
RateAmounts {
BaseGuestAmounts {
minimumAdultTravelers
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees {
value
currencyCode
decimalPlaces
}
}
}
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"updateSpaceTypeRate": {
"isActive": true,
"RatePeriods": [
{
"minLOS": 1,
"maxLOS": null,
"startDate": "2022-10-11",
"endDate": "2022-10-20",
"timeUnit": "DAILY",
"RateAmounts": {
"BaseGuestAmounts": [
{
"minimumAdultTravelers": 2,
"AmountAfterTaxesAndFees": {
"value": 12900,
"currencyCode": "USD",
"decimalPlaces": 2
}
}
]
}
},
{
"minLOS": 2,
"maxLOS": 2,
"startDate": "2022-10-11",
"endDate": "2022-10-20",
"timeUnit": "FULL_DURATION",
"RateAmounts": {
"BaseGuestAmounts": [
{
"minimumAdultTravelers": 2,
"AmountAfterTaxesAndFees": {
"value": 21900,
"currencyCode": "USD",
"decimalPlaces": 2
}
}
]
}
},
{
"minLOS": 3,
"maxLOS": 3,
"startDate": "2022-10-11",
"endDate": "2022-10-20",
"timeUnit": "FULL_DURATION",
"RateAmounts": {
"BaseGuestAmounts": [
{
"minimumAdultTravelers": 2,
"AmountAfterTaxesAndFees": {
"value": 30900,
"currencyCode": "USD",
"decimalPlaces": 2
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
This example sets SpaceTypeRate with multiple RatePeriods that define a price based on a combination of DAILY and FULL_DURATION bases.
These RatePeriod combinations define progressive Length-of-Stay based pricing for this RatePlan and SpaceType combination.
The FULL_DURATION timeUnit defines that the RateAmounts specified are the price for the entire qualifying duration.
For example, if a single Traveler wanted to book a one night stay from 2022-10-12 to 2022-10-13, they would be offered a price of $129.00 in this example, because they only qualify for the first RatePeriod with a minLOS of 1.
If this Traveler then extended their stay from 2022-10-12 to 2022-10-14, they would be offered a price of $219.00 because they qualify for the second RatePeriod defined with a minLOS of 2. Note the "timeUnit": "FULL_DURATION" field value.
Override a RatePlan
mutation {
setSpaceTypeRatePeriodOverrides(payload: {
RateOverrides: [
{
propertyId: "PROP-b7b05bd8-f9f8-5424-8ab4-3b41c4c4b74e",
ratePlanId: "RATE-3e852046-5e10-5ec4-bcdd-5a6073ee5084",
spaceTypeId: "SPTP-a1e3c546-97af-5f9e-9f88-13ae0cc9f296",
date: "2022-10-01",
GeneralOverrides: {
stopSell: false,
closedToArrival: false,
closedToDeparture: false
},
ConditionalOverrides: [
{
minLOS: 1,
timeUnit: DAILY,
RateAmounts: {
BaseGuestAmounts: [{
minimumAdultTravelers: 2,
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees: {
value: 13900,
currencyCode: USD,
decimalPlaces: 2
}
}]
}
}
]
}
]
})
{
date
ConditionalOverrides {
minLOS
timeUnit
RateAmounts {
BaseGuestAmounts {
minimumAdultTravelers
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees {
value
currencyCode
decimalPlaces
}
}
}
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"setSpaceTypeRatePeriodOverrides": [
{
"date": "2022-10-01",
"ConditionalOverrides": [
{
"minLOS": 1,
"timeUnit": "DAILY",
"RateAmounts": {
"BaseGuestAmounts": [
{
"minimumAdultTravelers": 2,
"AmountAfterTaxesAndFees": {
"value": 13900,
"currencyCode": "USD",
"decimalPlaces": 2
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
}
This example uses a RateOverride to make an adjustment to a single day’s price and conditions. The RateOverride entity can be used to override the RateAmounts previously set in a SpaceTypeRatePlan configuration using the ConditionalOverrides field.
The GeneralOverrides field can be used enable or disable availability of a RatePlan for a date based on certain conditions.
In this example, the BaseGuestAmount set for two Travelers with a minLOS value of 1 and a timeUnit of DAILY is being overridden and set to $139.00.
Apply a Stop Sell
mutation {
setSpaceTypeRatePeriodOverrides(payload: {
RateOverrides: [
{
propertyId: "PROP-b7b05bd8-f9f8-5424-8ab4-3b41c4c4b74e",
ratePlanId: "RATE-3e852046-5e10-5ec4-bcdd-5a6073ee5084",
spaceTypeId: "SPTP-a1e3c546-97af-5f9e-9f88-13ae0cc9f296",
date: "2022-10-01",
GeneralOverrides: {
stopSell: true,
}
}
]
})
{
Property {
id
}
SpaceType {
id
}
RatePlan {
name
}
date
GeneralOverrides {
stopSell
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"setSpaceTypeRatePeriodOverrides": [
{
"Property": {
"id": "PROP-b7b05bd8-f9f8-5424-8ab4-3b41c4c4b74e"
},
"SpaceType": {
"id": "SPTP-a1e3c546-97af-5f9e-9f88-13ae0cc9f296"
},
"RatePlan": {
"name": "-10% on taxes"
},
"date": "2022-10-01",
"GeneralOverrides": {
"stopSell": true
}
}
]
}
}
This example uses a RateOverride to make a SpaceTypeRate unavailable for sale on a specific date. By using the GeneralOverrides.stopSell property and setting it to true, any query for availability at this property will no longer return the overridden SpaceTypeRate as a bookable Product.
Retrieve Rate Breakdown
{
PropertiesConnection(
query: {PropertyIdList: ["PROP-b7b05bd8-f9f8-5424-8ab4-3b41c4c4b74e"]}
) {
edges {
node {
RatePlansConnection(
query: {RatePlanIdList: ["RATE-3e852046-5e10-5ec4-bcdd-5a6073ee5084"]}
) {
edges {
node {
id
SpaceTypeRates {
SpaceType {
id
}
DailyRates {
date
DayRateFromRatePeriods {
closedToArrival
stopSell
closedToDeparture
minLOS
maxLOS
timeUnit
RateAmounts {
BaseGuestAmounts {
minimumAdultTravelers
minimumChildTravelers
minimumInfantTravelers
minimumSeniorTravelers
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees {
value
currencyCode
decimalPlaces
}
}
AdditionalGuestAmounts {
AmountPerAdultTraveler {
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees {
value
currencyCode
decimalPlaces
}
}
}
}
}
DayRateOverrides {
SpaceTypeRateOverrides {
SpaceType {
id
}
GeneralOverrides {
closedToArrival
stopSell
closedToDeparture
}
ConditionalOverrides {
closedToArrival
stopSell
closedToDeparture
minLOS
maxLOS
timeUnit
RateAmounts {
BaseGuestAmounts {
minimumAdultTravelers
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees {
value
currencyCode
decimalPlaces
}
}
AdditionalGuestAmounts {
AmountPerAdultTraveler {
AmountAfterTaxesAndFees {
value
currencyCode
decimalPlaces
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"PropertiesConnection": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"RatePlansConnection": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"id": "RATE-3e852046-5e10-5ec4-bcdd-5a6073ee5084",
"SpaceTypeRates": [
{
"SpaceType": {
"id": "SPTP-a1e3c546-97af-5f9e-9f88-13ae0cc9f296"
},
"DailyRates": []
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
The Rate configuration offered by the network can be complex. This example shows a query that can be used to retrieve the current Rate configuration for a specific RatePlan at a Property as a day-by-day breakdown using the DailyRates field.
The response breaks out the underlying RatePeriod configuration in the DayRatesFromRatePeriods field and corresponding RateOverrides.
The RateOverride data can be overlaid over the DayRatesFromRatePeriods to get a flattened view of the current Rate configuration being offered to Travelers for booking.
This is useful when building a “Rate Grid” interface that allows users to make detailed changes to their Rate configuration for a Property on the network.
Product Examples
Complete detail of our entire schema and each individual field along with its type can be found by exploring our GraphQL IDE included with each node or accessed through our extranet.
Product Availability
query {
PropertiesConnection( query: {
PropertyIdList: ["PROP-20c7c5f5-8b11-56aa-aba3-9f3554c8de14"]
}){
edges {
node {
id
name
ProductsConnection(query: {
startDate: "2019-03-01",
endDate: "2019-03-02",
TravelerGroups: [{
TravelerCount: { adults: 1 },
TravelerAges: [22],
}]
}) {
edges {
node {
id
startDate
endDate
RatePlan {
id
name
}
SpaceType {
id
name
}
TotalPrice {
AmountBeforeTaxesAndFees {
value
decimalPlaces
currencyCode
ConvertTo(currency: EUR) {
value
decimalPlaces
currencyCode
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"PropertiesConnection": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"id": "PROP-20c7c5f5-8b11-56aa-aba3-9f3554c8de14",
"name": "Hotel Arise",
"ProductsConnection": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"startDate": "2019-03-01",
"endDate": "2019-03-02",
"RatePlan": {
"id": "RATE-ea95a96b-c222-454b-b303-6940a909d5d2",
"name": "Off-Season Rate"
},
"SpaceType": {
"id": "SPTP-eea2684a-f050-4def-abd1-c70e43ad1eb6",
"name": "Premiere Suite"
},
"TotalPrice": {
"AmountBeforeTaxesAndFees": {
"value": 23400,
"decimalPlaces": 2,
"currencyCode": "USD",
"ConvertTo": {
"value": 23803767,
"currencyCode": "EUR",
"decimalPlaces": 5
}
}
}
}
},
{
"node": {
"startDate": "2019-03-01",
"endDate": "2019-03-02",
"RatePlan": {
"id": "RATE-ea95a96b-c222-454b-b303-6940a909d5d2",
"name": "Off-Season Rate"
},
"SpaceType": {
"id": "SPTP-atr2684a-f878-5def-abd2-w41e09fg11b6",
"name": "King Room"
},
"TotalPrice": {
"AmountBeforeTaxesAndFees": {
"value": 12900,
"decimalPlaces": 2,
"currencyCode": "USD",
"ConvertTo": {
"value": 1311741,
"currencyCode": "EUR",
"decimalPlaces": 5
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
A Product is a combination of a Rate and Availability that a Traveler can book to create a Reservation.
To search for Products at a Property we can extend the Find Property query to include ProductsConnection.
A query for Products requires three parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| startDate | The start date of the product (equivalent to the check-in date) |
| endDate | The end date of the product (equivalent to the check-out date) |
| TravelerGroups | Groups of Travelers that each need their own Space |
Each price can be displayed in a different currency using the ConvertTo field. The supported currencies are USD, EUR and GBP. Exchange rates are updated daily.
Reservation Examples
Complete detail of our entire schema and each individual field along with its type can be found by exploring the Playground IDE included with each node.
Create Reservation
mutation {
createReservation( payload: {
propertyId: "PROP-d4d6d2b6-3e5a-5683-8c90-eab678ba9c9a",
startDate: "2022-01-16",
endDate: "2022-01-18",
ContactPerson: {
Person: {
PersonName: {
surname: "Lamb",
Given: "Alex"
},
Email: {
address: "alex@arise.travel"
}
}
}
SpaceStays: [
{
spaceTypeId: "SPTP-41547dc3-fac1-45d9-b89c-b635160a3970",
startDate: "2022-01-16",
endDate: "2022-01-18",
TravelerCount: {
adults: 2,
},
Traveler: {
PersonName: {
surname: "Lamb",
Given: "Alex"
}
}
}
]
}){
id
Property {
id
name
}
startDate
endDate
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"createReservation": {
"id": "RSRV-5ddb91b0-ee9d-5488-a218-4f2deaa64ede",
"Property": {
"id": "PROP-c55f8f8a-9939-46a0-b20a-700338088ab4",
"name": "Sample"
},
"startDate": "2022-01-16",
"endDate": "2022-01-18"
}
}
}
A single Reservation can contain multiple SpaceStays. Each SpaceStay can have different Travelers, start / end dates and different RatePlan and SpaceType assignments.
In order to reserve a specific Product, a propertyId must be provided, along with a ratePlanId and spaceTypeId for each SpaceType in the payload object.
The response to this mutation can contain the id of this new Reservation beginning with RSRV.
Modify Reservation
mutation {
updateReservation( query: {
reservationId: "RSRV-5ddb91b0-ee9d-5488-a218-4f2deaa64ede"
},
payload: {
ContactPerson: {
Person: {
PersonName: {
surname: "El Manawy",
Given: "Nadim"
},
Email: {
address: "nadim@arise.travel"
}
}
}
}){
id
ContactPerson {
Person {
PersonName {
surname
Given
},
Email {
address
}
}
}
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"modifyReservation": {
"id": "RSRV-5ddb91b0-ee9d-5488-a218-4f2deaa64ede",
"ContactPerson": {
"Person": {
"PersonName": {
"surname": "El Manawy",
"Given": "Nadim"
},
"Email": {
"address": "nadim@arise.travel"
}
}
}
}
}
}
A Reservation can be modified by using it’s reservationId and sending updated fields in the payload object.
The mutation in this example is updating the ContactPerson for the Reservation that was created in the previous example.
Cancel Reservation
mutation cancelReservation {
cancelReservation(query: {
reservationId: "RSRV-70f5eb9c-9feb-555d-8931-6b1580acbae6",
}){
Property {
id
name
}
Partner {
id
name
}
startDate
endDate
status
createdOn
cancelledOn
id
}
}
The expected response:
{
"data": {
"cancelReservation": {
"Property": {
"id": "PROP-d4d6d2b6-3e5a-5683-8c90-eab678ba9c9a",
"name": "Sample"
},
"Partner": {
"id": "PART-1e0ddd4d-eeee-58fa-b4de-dfb08057ccdd",
"name": "My Cloud PMS"
},
"startDate": "2022-01-16",
"endDate": "2022-01-18",
"status": "CANCELLED",
"createdOn": "2022-06-08T16:47:13.000Z",
"cancelledOn": "2022-09-20T14:19:19.000Z",
"id": "RSRV-6cdad485-1ad5-535f-afed-95c4165eb30a"
}
}
}
A Reservation can be cancelled by using it’s reservationId.

